Installing the Remote Services Package#
The Gurobi Remote Services package must be installed on all of the machines that will be part of your cluster. This includes the Compute Server nodes, the Distributed Worker nodes, and the Cluster Manager.
The first step is to download the installer from our download page. You will need to find your platform and choose the corresponding file to download.
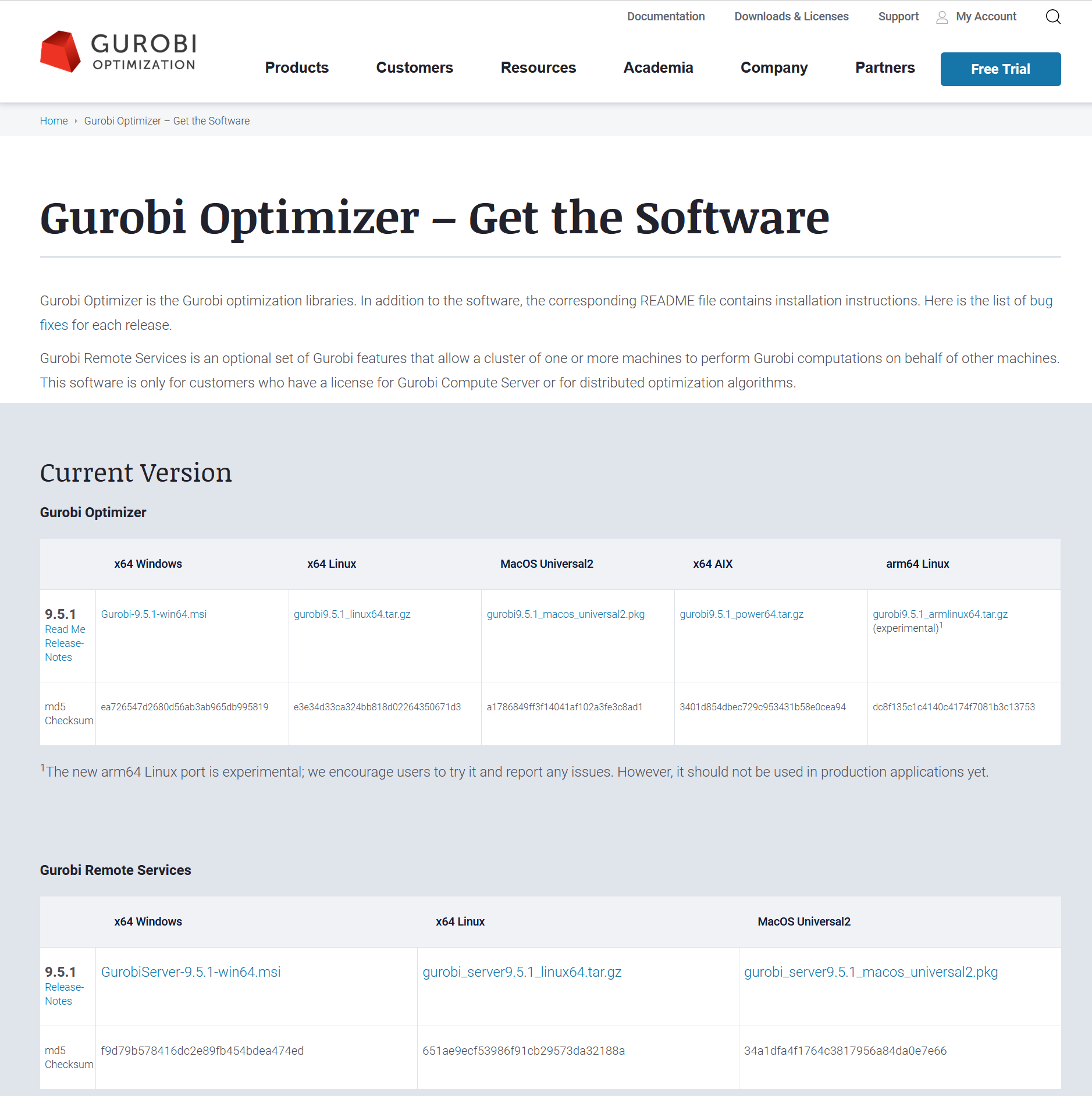
Make a note of the name and location of the downloaded file.
Your next step will depend on your platform:
Linux Installation#
On Linux, your next step is to choose a destination directory. We
recommend /opt for a shared installation (you may need administrator
privileges), but other directories will work as well. Copy the Remote
Services distribution to the destination directory and extract the
contents. Extraction is done with the following command:
tar xvfz gurobi_server11.0.0_linux64.tar.gz
This command will create a sub-directory gurobi_server1100/linux64
that contains the complete Linux Remote Services distribution. Assuming
that you extracted the Gurobi server archive in the /opt directory,
your <installdir> (which we’ll refer to throughout this document)
will be /opt/gurobi_server1100/linux64.
The Gurobi Optimizer makes use of several executable files. In order to
allow these files to be found when needed, you will have to modify your
search path. Specifically, your PATH environment variable should be
extended to include <installdir>/bin. Users of the bash shell
should add the following line to their .bashrc file:
export PATH="${PATH}:/opt/gurobi_server1100/linux64/bin"
Users of the csh shell should add the following line to their .cshrc
file:
setenv PATH "${PATH}:/opt/gurobi_server1100/linux64/bin"
You’ll need to close your current terminal window and open a new one after you have made these changes in order to pick up the new settings.
In some Linux distributions, applications launched from the Linux
desktop won’t read .bashrc (or .cshrc). You may need to set the
Gurobi environment variables in .bash_profile or .profile
instead. Unfortunately, the details of where to set these variables vary
widely among different Linux distributions. We suggest that you consult
the documentation for your distribution if you run into trouble.
macOS Installation#
On macOS, your next step once you’ve downloaded the Gurobi Remote
Services package from our website (e.g.,
gurobi_server11.0.0_macos_universal2.pkg for Gurobi 11.0.0) is to
double-click on the installer and follow the prompts. By default, the
installer will place the Gurobi Remote Services 11.0.0 files in
/Library/gurobi_server1100/macos_universal2 (note that this is the
system /Library directory, not your personal /Library
directory). Your <installdir> (which we’ll refer to throughout this
document) will be /Library/gurobi_server1100/macos_universal2.
Windows Installation#
On Windows, your next step is to double-click on the Gurobi Remote
Services installer that you downloaded from our website (e.g.,
GurobiServer-11.0.0-win64.msi for Gurobi 11.0.0).
Note: if you selected Run when downloading you’ve already run the installer and don’t need to do it again.
By default, the installer will place the Gurobi 11.0.0 files in
directory c:/gurobi_server1100/win64. The installer gives you the
option to change the installation target. We’ll refer to the
installation directory as <installdir>.